The Fundamental Foundation of Riding
The Basics of mtb & dirt bike riding position, utilizing AH-HA© (Ankles. Hips. Hands. Awareness.© methods.)
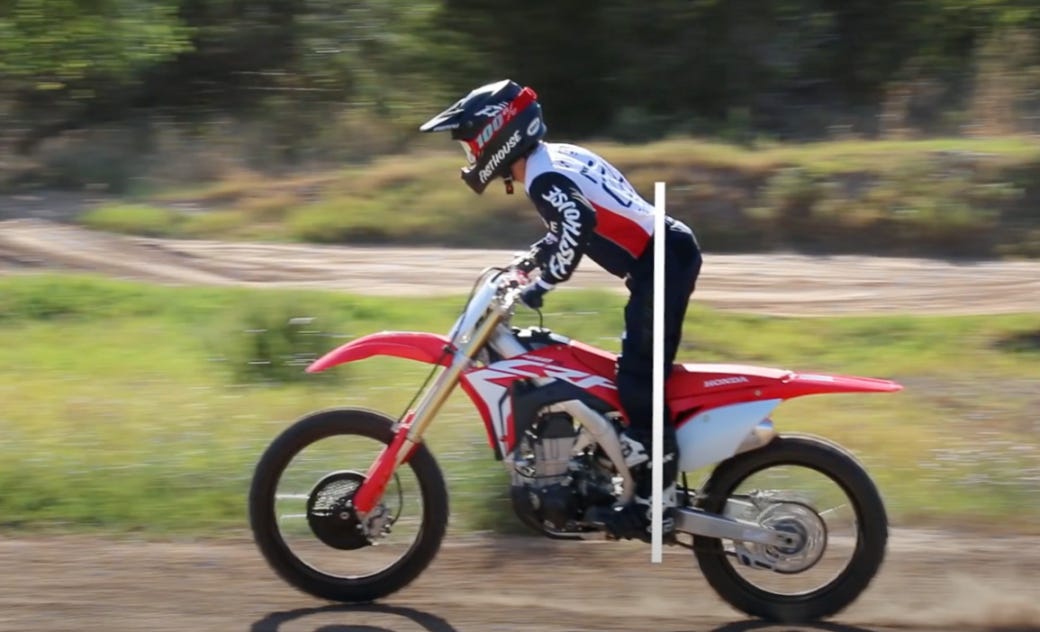
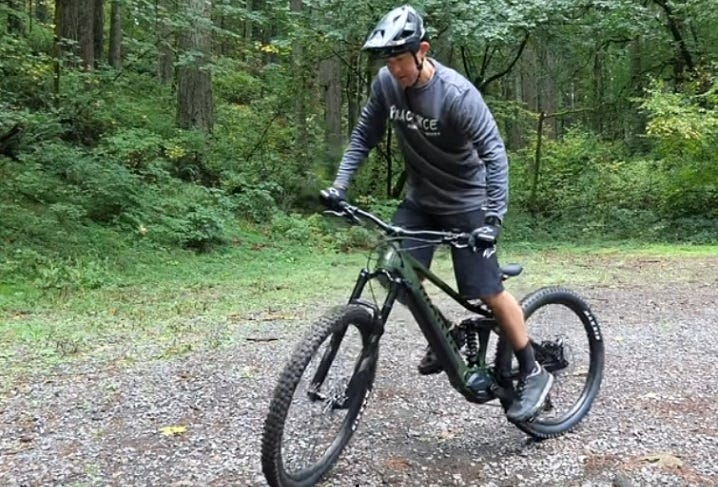
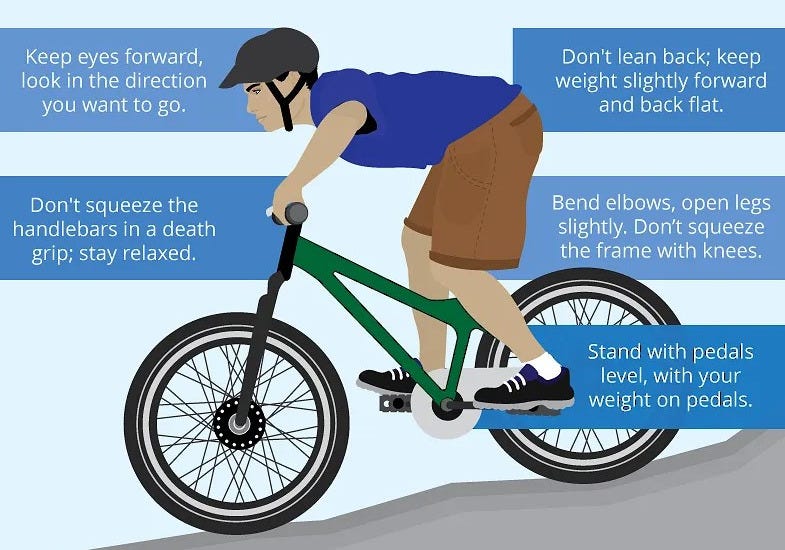
Body Position
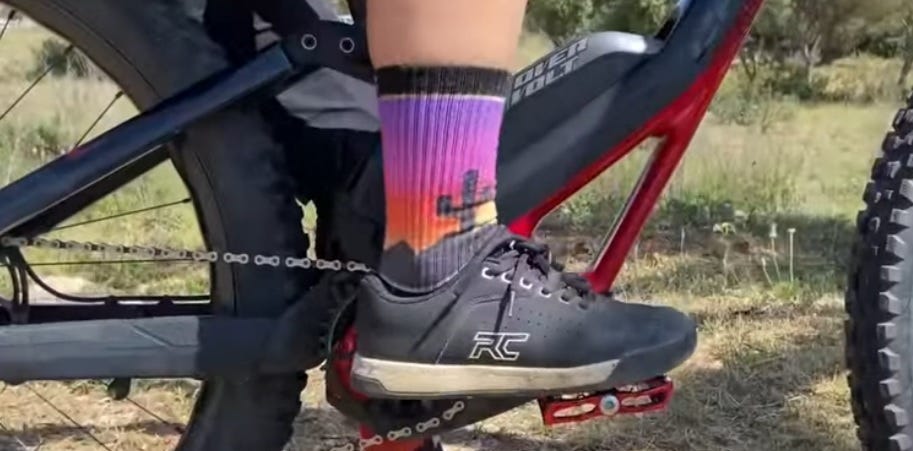
Ankle-foot placement; applying pressure and creating flexibility
(utilizing the balls of the feet)
Hips before knees (bending at the hips or Hinging/Rotating, instead of just bending the knees) Leading with the head.
Hands on the bar/controls (bars neutral not rolled too far forward or back)
Elbows elevated for proper leverage/control. Elbows and shoulders should absorb the energy being produced.Body-Bike separation (un-weighting/unloading the saddle and weighting/loading the pedals and-or pegs) This increases stability by loading/weighting the bikes Center of Mass (CoM) and shifting the Center of Gravity. Which manipulates the Center of Pressure in relation to the Center of Gravity.
Balance
Both Dynamic and Static balance are critical for control. Using pressure and subtle movement of the body to counter-balance the bike (manipulating the Center of Gravity) in order to stay upright- either when moving or stationary.
Standing slightly (weight through the pedals) and keeping hand pressure light on the bars (avoid using a ‘death-grip’) which negatively affects the natural forces- (gyroscopic, vertical, horizontal and centrifugal) which induces instability.
Output
Awareness. Anticipation. Reaction. A rider needs to utilize Situational Awareness at all times while riding in order to Anticipate what is occurring at the moment and what will and can occur in the next moment. Being aware and anticipating changes allows for proper Reaction.
Adaptation. Deliberate and Purposeful Practice. Versatility increases control.
Power delivery (propulsion) and pedal position. Smooth pedaling and ratcheting the pedals when necessary so as not to be caught in the 5-6-7 O’clock or 11-12-1 O’clock positions. Maintaining near level pedals
(except for tight corners) for optimal control and stability.Braking with variable, light, progressive pressure. (not grabbing and stabbing on the brake levers) The improper use (too great) of braking force, the quicker the Load-Transfer, which creates significant instability and potential loss of control.